The Impact of the Energy Crisis on the Food and Beverage Industry
Food and beverage manufacturing is a vital industry to the economy of any country, accounting for more than 10% of the world's GDP, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). In the food and beverage industry, the energy crisis has adversely affected several aspects, including production, distribution, and the cost of quality and food safety. Recent increases in energy prices, limited energy resources, and global climate change have put increased pressure on industries to reduce energy consumption. Growing, harvesting, processing, packaging, transportation, and food storage consumes substantial energy. The result has been higher costs for producers, in most circumstances forcing them to pass these costs along to consumers, thus making food more expensive and less accessible.
In 2022, all food price categories tracked by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Economic Research Service (ERS) increased by more than 5 percent. Food-at-home prices increased by 11.4 percent, and food-away-from-home prices increased by 7.7 percent. The USDA estimates that food prices increased by 9.9 percent, predicting food inflation to remain high for 2023 at 7.1 percent.
The energy crisis also affects Europe; Eurostat reports that the food inflation rate for January 2023 was 18.4%, and the energy inflation rate was 20.6%.
Food and beverage companies are turning to digital solutions to combat the effects of the energy crisis and implementing sustainable methods to reduce their energy consumption and costs.
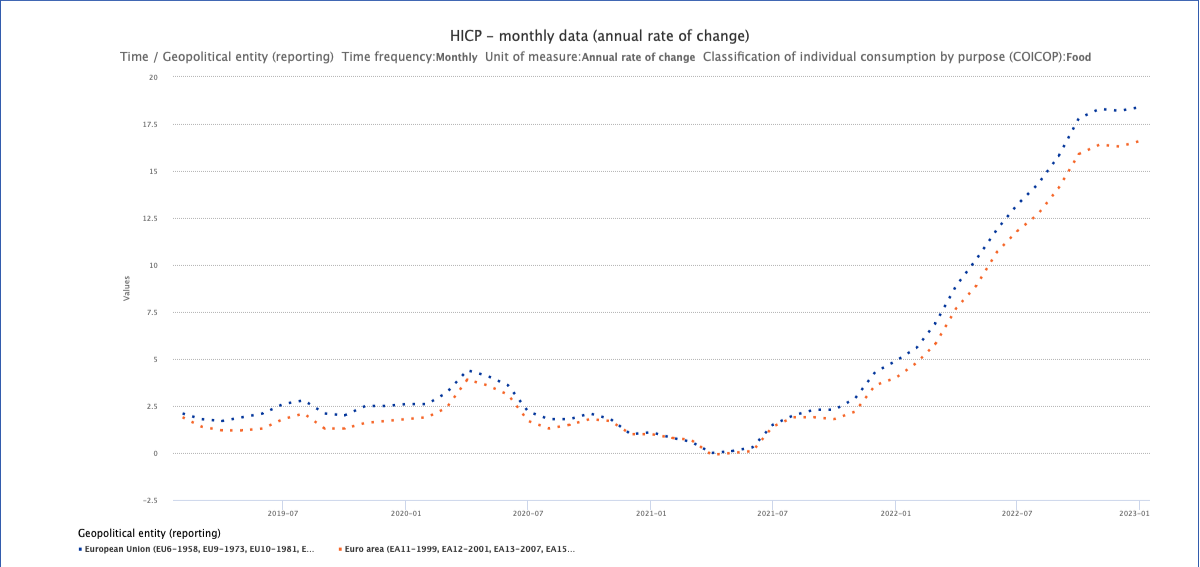
Figure 1: The evolution of Food inflation rate in Europe
The Impact of the Energy Crisis on the Cost of Quality
The cost of energy is an integral component of the cost of quality. Energy is essential to the production process and food preservation. Any increase in energy costs will lead to a rise in the overall cost of quality, both directly and indirectly. Direct costs include energy use, and indirect costs such as production delays, rework, and recalls.
The food industry can take several measures to mitigate the effects of the energy crisis on the cost of quality, including:
1. Efficiency in energy use: Invest in more energy-efficient equipment, such as high-efficiency boilers, ovens, retorts, and refrigeration units. Eventually, these upgrades may result in significant savings, although requiring considerable capital expenditure at inception.
2. Process optimization: Reducing energy consumption by optimizing production schedules and reducing downtime between production runs.
3. Renewable energy sources: Investigate alternatives and renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power. Initially, these alternatives may seem more expensive, but over time they are likely to prove more cost-effective and contribute to sustainability.
Among the many benefits of using renewable energy are the following:
-
Lower environmental impact
-
Reduced operating costs
-
An increase in production capacity
-
Improved brand recognition
-
Enhanced customer loyalty
-
An increase in shareholder value
-
Carbon footprint reduction
-
Increased employee morale
4. Management of the supply chain: Identify energy-efficient transportation options and devise sustainable packaging options with suppliers.
5. Training and engagement: Provide employees with information and training on energy conservation and encourage them to identify and report potential energy waste.
Through these mitigation strategies, F&B companies can reduce their energy consumption and overall cost of quality while ensuring the safety and quality of their food products. Ensuring that the food sector continues to meet quality and safety objectives, continuously monitoring and evaluating these strategies' effectiveness will be imperative.
Combating The Energy Crisis Through Digital Solutions
The food industry consumes significant energy for heating, cooling, and refrigeration. Food manufacturers and processors face substantial challenges meeting safety and quality requirements without reliable, sustainable energy resources.
Food and Beverage companies are finding it challenging to meet the demand for their products as energy costs and availability increase. An inevitable delay in production leads to reduced production capacity and increased cost. The fall in production capacity may increase work pressure on employees, causing fatigue and increased errors in the production process. Food safety is a significant product manufacturing, packaging, and distribution concern. Food organizations must maintain high production standards, including adequate temperatures throughout the year, to avoid food spoilage during storage or transportation. Maintaining the proper temperature, humidity, and other pertinent parameters for guaranteeing food safety in production facilities has become difficult. These challenges pose a severe risk to the safety and quality of food products.
Food and beverage companies may suffer financial losses due to excessive processing through thermal technologies. Excessive heat treatment can increase energy consumption, resulting in higher operating costs. As a result of overprocessing, the quality of the final product can be reduced, leading to increased levels of waste, product rework, and the possibility of recalls. In addition, overprocessing may affect the final product's taste, texture, and nutritional value, affecting customer satisfaction and loyalty. Consequently, sales and revenues can be affected.
By monitoring and controlling thermal processing operations in real-time, smart process control systems can assist in resolving these issues. The use of sensors and analytics helps operators optimize processing parameters to minimize overprocessing and reduce energy consumption by monitoring critical process variables such as temperature, pressure, and flow rate.
In addition to providing real-time feedback and control, smart process control can help ensure that the final product meets quality and safety standards and minimize process variability. As a result, food and beverage companies may be able to increase their sales and revenue by improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
The use of digital solutions for data analysis allows manufacturers to monitor their critical control points (CCP), energy consumption, and production processes in real time, identify trends and potential problems, taking preventative measures before they occur. By providing insights into energy consumption patterns, cloud-based solutions can help manufacturers identify sources of energy waste and optimize energy use. These solutions assist with identifying deviations in production processes, which can lead to the early detection and alleviation of potential food safety risks.
Furthermore, cloud-based solutions provide manufacturers access to real-time data from their supply chain partners, enhancing transparency and collaboration. As a result, all parties are subject to the same quality and safety standards, regardless of the energy crisis.
Sustainability Measures Alleviating the Energy Crisis
The food and beverage industry are one of the most energy-intensive sectors in the world, consuming a great deal of electricity, natural gas, and other fossil fuels. Due to the recent energy crisis, however, the cost of these resources has increased significantly, which has resulted in a significant increase in the food manufacturers' production costs. Consequently, food manufacturers face more significant challenges in maintaining high food safety and quality levels while keeping low production costs. Additionally, global population growth and the rising demand for safe and high-quality food make it more challenging to meet those demands while reducing the environmental impact. The energy crisis has prompted a shift towards sustainability initiatives aimed at reducing its impact on food safety, quality professionals, and the food industry.
Sustainability programs such as implementing energy-efficient systems and processes play an essential role in combating and reducing the impacts of the energy crisis on food safety, quality professionals, and the food industry in general. Increasingly, manufacturers are investing in energy-efficient equipment, smart digital technologies, and techniques that reduce their energy consumption and operating costs, thereby reducing their carbon footprints.
Sustainable farming practices are another initiative to counteract the effects of the energy crisis on the food sector. As part of this effort, F&B companies are implementing organic farming methods that reduce the utilization of highly energy-intensive equipment, synthetic fertilizers, and pesticides. For example, some manufacturers contract with local farmers to source their ingredients. Consequently, the carbon footprint associated with transportation is reduced, and the raw ingredients used in the products are fresh, of high quality, and readily available.
Food and Beverage manufacturers are incorporating renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower to reduce reliance on traditional energy supplies. For instance, General Mills, one of the world's leading food manufacturers, plans to source 100% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2030. In implementing this initiative, the company will be able to reduce its environmental impact while maintaining high food safety and quality standards.
Using energy-efficient equipment is another sustainability initiative that food manufacturers are adopting. Nestle, for example, has installed energy-efficient lighting systems in its factories, resulting in a reduction of 14% in its electricity consumption. Taking this step has assisted the company in reducing its environmental degradation footprint while achieving its food safety and quality goals.
The energy crisis has also prompted many food manufacturers to adopt sustainable packaging solutions. Using sustainable packaging solutions reduces the environmental impact of packaging and ensures food safety and quality. PepsiCo, for instance, has set a goal of using 100% recyclable, compostable, or biodegradable packaging by 2025, aimed at reducing its environmental impact through its sustainable packaging practices.
Conclusion
The food and beverage industry significantly contributes to the global economy. Still, it has been negatively impacted by the energy crisis, resulting in higher production and distribution costs, lower production capacity, and increased food prices. The food industry has turned to digital solutions, renewable energy sources, process optimization, and training employees on energy conservation to alleviate the constraining effects of declining energy availability. Incorporating these eco-friendly strategies can significantly reduce the cost of quality while maintaining the safety and quality of food products. Cloud-based intelligent digital solutions, powered by technologies like AI (Artificial Intelligence), provide valuable insights into energy consumption patterns, enabling manufacturers to identify sources of energy waste and optimize energy use. Furthermore, manufacturers invest in energy-efficient equipment and techniques that reduce energy consumption and operating costs. These sustainable practices are essential in combating and reducing the impacts of the energy crisis on food safety, quality professionals, and the food industry in general.
To learn more, feel free to contact us below :




